
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100083, China
2 College of Materials Science and Opto-Electronic Technology, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 Beijing Key Laboratory of Genome and Precision Medicine Technologies, Beijing 100101, China
Ion sensitive field effect transistor (ISFET) devices are highly accurate, convenient, fast and low-cost in the detection of ions and biological macromolecules, such as DNA molecules, antibodies, enzymatic substrates and cellular metabolites. For high-throughput cell metabolism detection, we successfully designed a very large-scale biomedical sensing application specific integrated circuit (ASIC) with a 640 × 640 ISFET array. The circuit design is highly integrated by compressing the size of a pixel to 7.4 × 7.4μm2 and arranging the layout of even and odd columns in an interdigital pattern to maximize the utilization of space. The chip can operate at a speed of 2.083M pixels/s and the dynamic process of the fluid flow on the surface of the array was monitored through ion imaging. The pH sensitivity is 33 ± 4 mV/pH and the drift rate is 0.06 mV/min after 5 h, indicating the stability and robustness of the chip. Moreover, the chip was applied to monitor pH changes in CaSki cells metabolism, with pH shifting from 8.04 to 7.40 on average. This platform has the potential for continuous and parallel monitoring of cell metabolism in single-cell culture arrays.Ion sensitive field effect transistor (ISFET) devices are highly accurate, convenient, fast and low-cost in the detection of ions and biological macromolecules, such as DNA molecules, antibodies, enzymatic substrates and cellular metabolites. For high-throughput cell metabolism detection, we successfully designed a very large-scale biomedical sensing application specific integrated circuit (ASIC) with a 640 × 640 ISFET array. The circuit design is highly integrated by compressing the size of a pixel to 7.4 × 7.4μm2 and arranging the layout of even and odd columns in an interdigital pattern to maximize the utilization of space. The chip can operate at a speed of 2.083M pixels/s and the dynamic process of the fluid flow on the surface of the array was monitored through ion imaging. The pH sensitivity is 33 ± 4 mV/pH and the drift rate is 0.06 mV/min after 5 h, indicating the stability and robustness of the chip. Moreover, the chip was applied to monitor pH changes in CaSki cells metabolism, with pH shifting from 8.04 to 7.40 on average. This platform has the potential for continuous and parallel monitoring of cell metabolism in single-cell culture arrays.
ASIC ISFET array pH monitoring ion imaging cell metabolism Journal of Semiconductors
2023, 44(2): 024101
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Integrated Optoelectronics, Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100083, China
2 College of Materials Science and Opto-Electronic Technology, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 101408, China
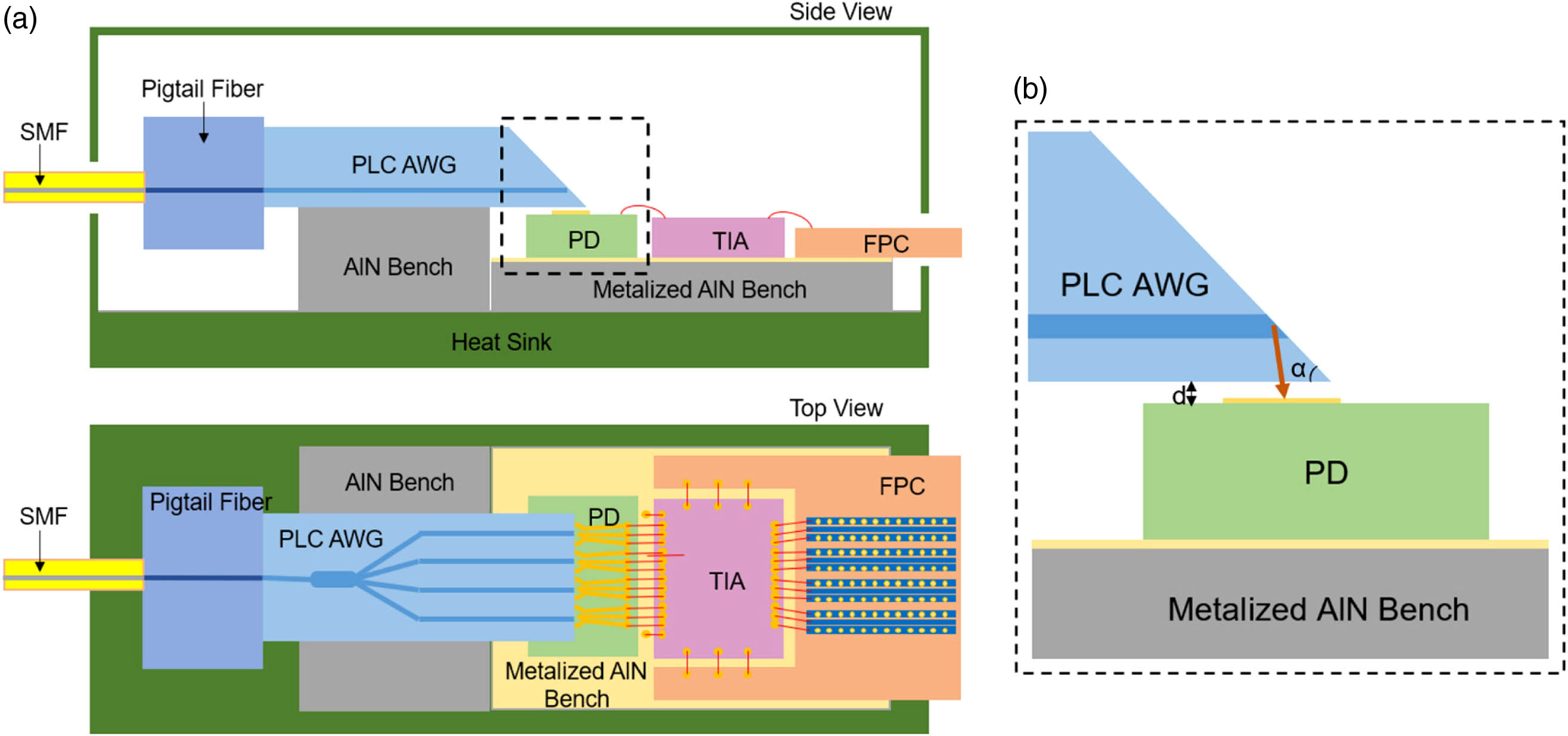
We demonstrate a low-cost hybrid integrated and compact 100 GBaud four-lane coarse wavelength division multiplexing (CWDM) receiver optical sub-assembly (ROSA) based on an arrayed waveguide grating de-multiplexer in the O band. To achieve the horizontal light coupling between the planar light-wave circuit (PLC) based arrayed waveguide grating de-multiplexer and photodetector array, a 42° polished facet is applied for total reflection. A flexible printed circuit with high-frequency coplanar waveguides is used for a power supply of trans-impedance amplifier and signal transmission. The fabricated CWDM ROSA module, whose size is , shows a 3 dB bandwidth of 21.2, 18.4, 19.6, and 19.3 GHz, respectively, in each lane. The overall symbol error rates are at a magnitude of for 25 GBaud four-level pulse amplitude modulation (PAM-4) transmission with an average input optical power of 5 dBm.
Photonics Research
2019, 7(7): 07000722
Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory on Integrated Optoelectronics, Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100083, China
We report a compact 2×2 Mach–Zehnder interferometer (MZI) electro-optic switch fabricated on a silicon-on-insulator using standard complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) processes. With a short modulation arm length of 200 μm, the crosstalk is reduced to 22 dB by the new modulation scheme of push–pull modulation with a pre-biased π/2 phase shift. The new modulation scheme can also work with a fast switching time of about 5.4 ns.
130.4815 Optical switching devices 130.3120 Integrated optics devices 200.4650 Optical interconnects Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(6): 061301
Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory on Integrated Optoelectronics, Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100083, China
We demonstrate a sub-nanosecond electro-optical switch with low crosstalk in a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) dual-coupled micro-ring embedded with p-i-n diodes. A crosstalk of -23 dB is obtained in the 20 \mu m-radius micro-ring with the well-designing asymmetric dual-coupling structure. By optimizations of the doping profiles and the fabrication processes, the sub-nanosecond switch-on/off time of <400 ps is finally realized under an electrical pre-emphasized driving signal. This compact and fast-response micro-ring switch, which can be fabricated by complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) compatible technologies, have enormous potential in optical interconnects of multicore networks-on-chip.
绝缘体上的硅 微环 电光调制器 等离子色散效应 光互连 130.3120 Integrated optics devices 250.6715 Switching 230.5750 Resonators 230.4000 Microstructure fabrication Chinese Optics Letters
2010, 8(8): 757





